

Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis/ Timely action
Table of Contents
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune illness that causes swelling and damage to joints, leading to pain and stiffness. It affects up to 1.3% of the US adult population or about 4.6 million people. It is more common in females and expands between 40 and 60.
Determination of Other risk factors, including a family history of the condition, obesity, and smoking, will be essential for early rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis.
Worldwide, an estimated 50 million people have rheumatoid arthritis.
Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis allows for prompt initiation of appropriate therapy, which can help to reduce pain, stiffness, and disability, improve quality of life, and slow down the development of the disease. Identification is done through careful medical history, physical tests, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
The necessary warning is that delaying detection can lead to increased joint damage and long-term health complications.
The diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, and it is essential to work with a rheumatologist or other healthcare professional who has experience with the condition.
Hence, in this article from drhealthandbeauty, we provide valuable information so that you can cooperate best with specialists to diagnose this disease.

Take action before it gets worse.
The Diagnostic Criteria for RA
Blood tests are used to help diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, monitor the effectiveness of treatment, and track disease activity.
Although blood tests are valuable diagnostic tools, they need higher accuracy.
In order to accurately recognize the disease, in addition to testing and imaging, the patient’s medical history must also be evaluated, including current symptoms, especially pain, swelling, and stiffness, their location, duration, and severity.
After examining the medical history, specialists will make a “differential diagnosis,” which attempts to rule out other similar and autoimmune diseases such as lupus, psoriatic arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis.
In the examination of the medical history for early detection of rheumatoid arthritis, they will also ask questions about the family history because, according to the research, people who have a family member with this disease will be more than two times more exposed to this disease than other people.
Equipping all facilities for timely diagnosis
General tests
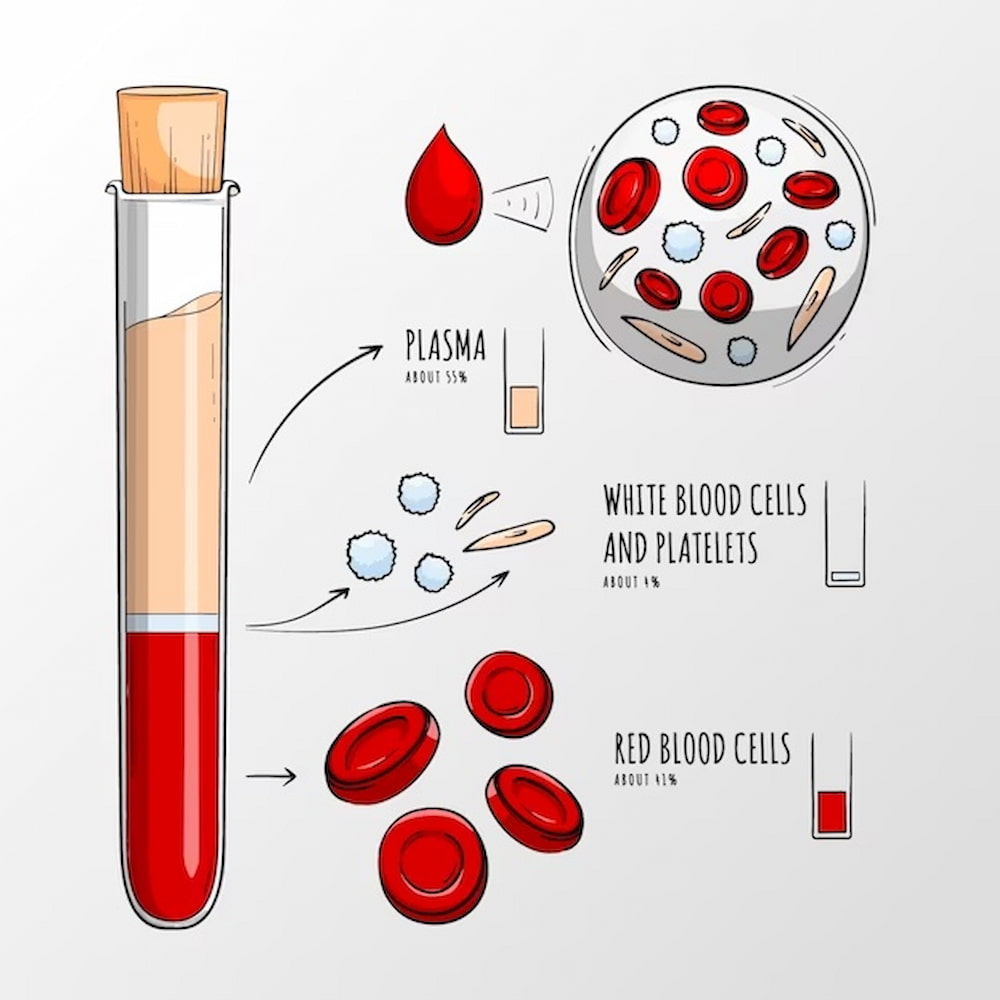
Complete blood count (CBC) test
In this test, which is common in determining autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, the amount of red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets are counted.
These cells are suspended in the plasma (thick yellow liquid of the blood).
.
- White blood cells: Normally, the number of these blood cells per microliter of blood is 5 to 10 thousand.
A white blood cell counts higher than this value indicates inflammation or infection.
However, It should be noted that Factors such as exercise, colds, and stress can temporarily increase the number of white blood cells.
- Red blood cells: The average number of red blood cells depends on gender.
In men, the average number of red blood cells is between 5 and 6 million per microliter, while in women, the average number of red blood cells is between 3.6 and 5.6 million per microliter of blood.
A small or large number of these cells is an estimate for diseases.
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit: Hemoglobin – the iron component of red blood cells – liable for oxygen delivery, is also counted For diagnostic testing.
The average number of hemoglobin in men is between 13-18 g/dL and in women 12-16 g/dL. Hematocrit evaluates the number of red blood cells as a percentage of total blood. Normal hematocrit is 40-55% in men and 36-48% in women.
Generally, the amount of hematocrit is three times the amount of hemoglobin in the blood.
A decrease in these values is a sign of anemia. MCV, MCH, and MCHC are red blood cell indices showing red blood cells’ size and hemoglobin content.
These indicators can provide a clue to recognize the possible cause of a person’s anemia.
Related: “How Can I Raise Iron Levels Fast?“
- Platelets: Platelets are significant components of the blood clotting process.
Many drugs that are prescribed to treat arthritis can reduce the number of platelets or affect their function.
The average platelet amount is 150-400 thousand per microliter of blood.
- Differential analysis of white blood cells: neutrophils increase in bacterial infections and acute inflammations, lymphocytes in viral infections, monocytes in chronic infections, and eosinophils in allergies and other diseases.
Moreover, they are one of the criteria to distinguish these diseases.
An increase in the number of eosinophils is called eosinophilia. Basophils comprise about 1 to 2% of white blood cells in total and are rarely elevated.
- Inflammation: During inflammation, there are changes in blood cell counts. The number of red blood cells may decrease, white blood cells may increase, and platelets may increase.
While anemia can be caused by inflammatory arthritis, it can also occur for other reasons, such as bleeding or iron deficiency.
Related: “How To Deal With Fatigue From Iron Deficiency?“
Only if other causes have been ruled out can a doctor interpret blood abnormalities as a sign of inflammation.
Blood chemistry tests
A chemistry panel is a series of experiments to evaluate the main functions of metabolism and Recognition of diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Related: “What Are The Red Flags Of Rheumatoid Arthritis?“
A group of tests is performed on serum (cell-free part of blood). Electrolytes and ionized salts in blood and tissue fluids (such as sodium, potassium, and chloride) are part of the chemistry panel.
Diagnostic tests also indicate heart risk, diabetes, kidney and liver function.
For example, if a person’s high blood creatinine indicates an abnormal kidney condition.
Creatinine is a waste substance found in the blood. Certain types of inflammatory arthritis, as well as some arthritis medications, can affect kidney function.
Related: “How Do You Treat Arthritis In The Hands?“
Uric acid is another diagnostic test in the chemistry panel. An increase in uric acid can be a sign of gout. These were just examples from the chemistry panel. The blood chemistry panel provides data about how the body is functioning.

Special tests
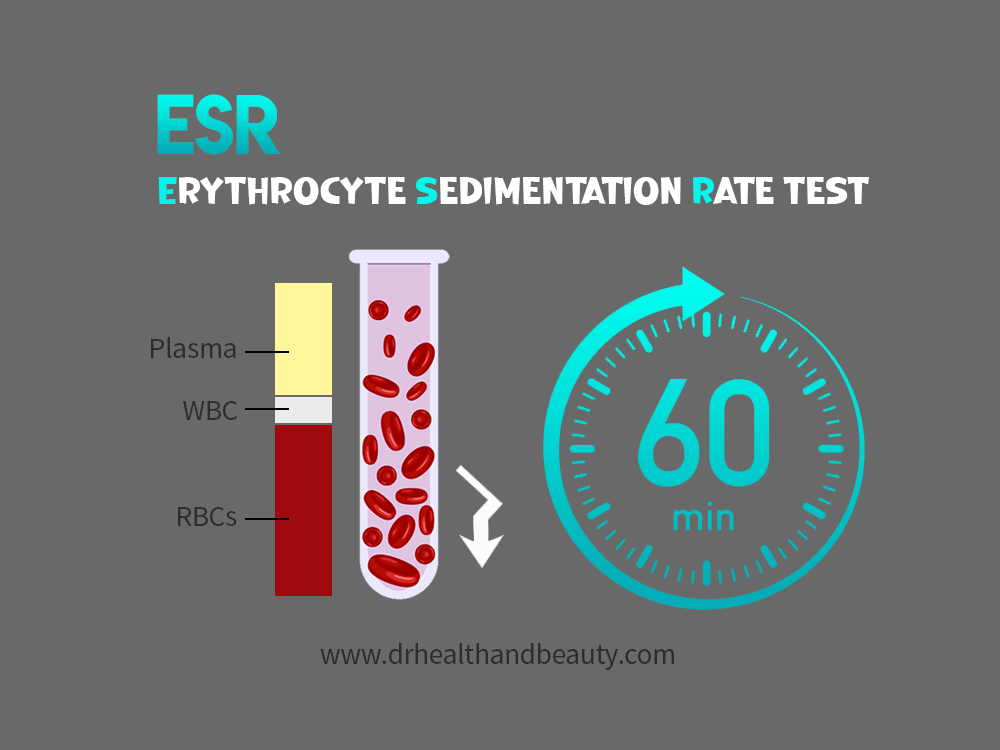
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test
This diagnostic test involves placing the blood sample in special tubes and checking the sedimentation rate of red blood cells.
If there is inflammation, the body secretes proteins into the blood that cause the red blood cells to clump together. As a result, heavier cells are deposited faster than normal cells.
In healthy adults, a rate of up to 20 mm/h is average (0-15 mm/h for men and 0-20 mm/h for women).
Inflammation significantly increases the rate of deposition. Since inflammation can indicate other diseases besides arthritis, this recognitional test is non-specific.
Rheumatoid factor (RF)
Rheumatoid factors are antibodies found in many patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid factors were discovered in the 1940s and became a considerable diagnostic tool in rheumatology.
Nearly 80% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis have rheumatoid factors in their blood. Usually, a high concentration of rheumatoid factor leads to severe diseases.
Rheumatoid factors may take months to appear in the blood. If the test is done early, the results may be harmful, so the test should be retested later.
In cases where patients have signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis, but their rheumatoid factor test is negative, doctors suspect other diseases mimicking rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid factors may also occur in response to other inflammatory or infectious diseases, although in these cases, the concentration of these factors is lower than that found in rheumatoid arthritis.
HLA Typing test
White blood cells may be tested for HLA-B27. This diagnostic test is standard in medical centers where transplantation is performed.
Also, HLA-B27 is a genetic marker attached to certain types of arthritis, mainly Ankylosing Spondylitis and Reiter’s Syndrome.
.
Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) test
This test is done to help diagnose rheumatic diseases like rheumatoid arthritis.
Certain patients or diseases, such as lupus, form antibodies to the nucleus of the microcosm’s cells. These antibodies are called anti-nuclear antibodies, which can be seen by placing the patient’s serum under a microscope.
A fluorescent substance is added to the serum so that it binds to the antibodies and makes them visible.
More than 95% of lupus patients have a positive ANA test.
Related: “10 Early Symptoms Of Lupus In Women“
50% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis have a positive result for the ANA test.
Also, people suffering from other diseases can have a positive result. For a definitive diagnosis, other criteria should be considered.
C-reactive protein (CRP)
This test measures the concentration of a specific protein secreted by the liver. It is for detecting inflammation and infection because this protein is present in blood serum during acute inflammation or infection.
CRP is considered a non-specific blood test. High amounts of this protein indicate acute inflammation in the body.
In inflammatory rheumatic illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, doctors use the CRP test to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and disease activity.
Antibody test against cyclic citrullinated peptide (Anti-CCP)
This test is one of the new blood tests used to corroborate the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
If the antibody is present at a high level in the body, the possibility of severe joint damage also increases.
Anti-DNA and Anti-Sm test
People with lupus develop antibodies against DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
There is a test to detect the presence of these antibodies. This test is an excellent diagnostic tool because anti-DNA antibodies are not found in people who do not have lupus.
Also, this test is suitable for monitoring the disease due to the increase or decrease of these antibodies with disease activity.
People with lupus form antibodies against another substance in the nucleus of cells called Smith (Anti-Sm).
Sm antibodies are also found only in patients with lupus. This test does not have a unique feature for monitoring the disease.
Conclusion
It is an essential warning that rheumatoid arthritis can cause long-term damage to the joints and severe damage to the whole body, accompanied by pain and disability.
If it is diagnosed late and is not controlled, it can change the shape of the body’s joints over time and lose part of their function.
The good news is that timely diagnosis and correct and timely treatment will significantly impact preventing long-term damage and maintaining normal joint function.
With current treatment options, most people can have reasonable control of their symptoms and slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.

